Python Developer Roadmap 2026: Skills, Tools, Frameworks & Career Guide

What to Learn, In What Order, and How Python Developers Grow Professionally
Python remains one of the most widely used programming languages across software development, backend systems, automation, data platforms, and AI-enabled applications. However, most online guides focus only on tools and frameworks, which leads to fragmented learning and poor career outcomes.
This document presents a structured, role-aligned roadmap for becoming a Python Developer, covering:
-
skill sequencing
-
tools and frameworks by purpose
-
professional expectations at each career level
-
certification positioning
-
salary progression
This guide is designed for beginners, career switchers, and early professionals, and reflects how Python development is practiced in real production environments.
What a Python Developer Role Actually Involves
A Python Developer is responsible for building, maintaining, and improving software systems using Python. The role typically includes:
-
writing backend logic and services
-
developing APIs
-
automating workflows and processes
-
integrating databases and external systems
-
maintaining code quality and performance
-
collaborating with frontend, DevOps, and product teams
Python Developers are commonly employed in:
-
backend web development
-
internal tooling and automation
-
platform and API development
-
data-intensive systems
Python itself is a foundation language, not a specialization. Career outcomes depend on how it is applied.
Python Developer Role: Practical Scope and Market Reality
Daily Responsibilities
A Python Developer’s daily work typically includes:
-
writing and maintaining backend logic and services
-
implementing APIs and integrating external systems
-
reading, modifying, and debugging existing codebases
-
working with databases and data models
-
handling configuration, environments, and dependencies
-
reviewing code and following team standards
-
collaborating with product, frontend, and infrastructure teams
The role involves problem resolution and system maintenance as much as new development.
Where Python Is Commonly Used
Python is widely used in:
- Backend web development
- API and microservice development
- Automation and internal tooling
- Data processing and pipelines
- Testing frameworks and scripts
- Platform and integration services
Python is chosen for its readability, flexibility, and large ecosystem.
Where Python Is Typically Not Used
Python is not the primary choice for:
- Low-level system programming
- Real-time embedded systems
- Performance-critical game engines
- Operating system kernels
- Front-end browser execution
In such domains, languages like C, C++, Rust, or JavaScript are more appropriate.
Types of Companies Hiring Python Developers
Python Developers are hired by:
-
software product companies
-
SaaS platforms
-
fintech and healthcare organizations
-
e-commerce and logistics firms
-
data-driven enterprises
-
startups building backend systems
-
enterprises maintaining internal automation tools
Hiring demand exists across both small teams and large organizations.
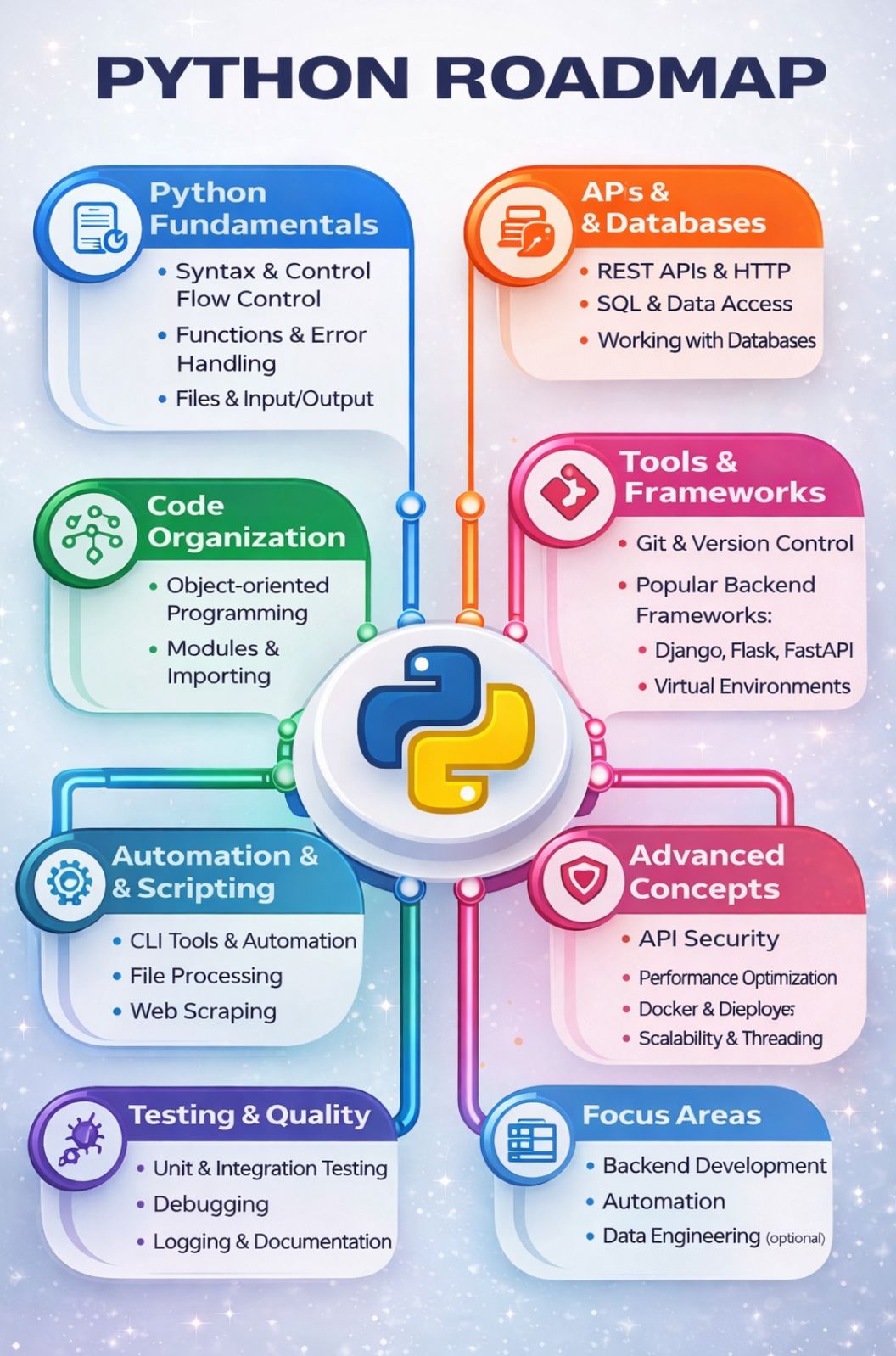
Skill Architecture of a Python Developer
Instead of learning randomly, Python skills should be built in layers, where each layer depends on the previous one.
Layer A: Language Control
These skills ensure full command over the Python language.
-
syntax and execution flow
-
data types and memory behavior
-
conditional logic and loops
-
functions and scope
-
exception handling
-
file input/output
Without this layer, developers struggle with debugging and code reliability.
Layer B: Program Structure
This layer focuses on writing maintainable and scalable code.
-
object-oriented programming
-
class design and inheritance
-
modules and packages
-
code reuse and separation of concerns
-
readable and documented code
Most production issues originate from weak structure, not weak syntax.
Layer C: System Interaction
This layer enables Python programs to interact with real systems.
-
REST APIs and HTTP concepts
-
database access and queries
-
configuration management
-
environment isolation
-
handling external services
This is where Python becomes professionally useful.
Recommended Learning Order (Critical Section)
The order of learning determines long-term success.
Correct order
-
Core Python language
-
Program structure and OOP
-
System interaction (APIs, databases)
-
Frameworks
-
Deployment concepts
Common mistake
-
learning frameworks before understanding Python internals
Frameworks simplify development but hide complexity. Learning them too early leads to shallow understanding.
Python Tools Categorized by Purpose
Instead of listing tools, it is more effective to understand why they exist.
Code Authoring
-
code editors and IDEs
-
syntax checking and formatting
Purpose: productivity and correctness
Dependency & Environment Management
-
virtual environments
-
dependency isolation
Purpose: reproducible and stable systems
Version Control
-
source code tracking
-
collaboration and rollback
Purpose: teamwork and code safety
Testing & Quality
-
unit testing
-
logging
-
debugging
Purpose: reliability and maintainability
Deployment & Runtime
-
application packaging
-
process management
-
containerization (basic understanding)
Purpose: running software in production environments
Python Frameworks: Usage-Based Explanation
Frameworks are not interchangeable; each exists for a specific problem space.
Django
-
full-featured backend framework
-
includes authentication, ORM, admin tools
Used when:
-
building large, structured applications
-
long-term maintainability is required
Flask
-
lightweight and flexible
-
minimal built-in assumptions
Used when:
-
building small services
-
requiring high customization
FastAPI
-
modern, performance-oriented
-
strong typing and API documentation
Used when:
-
building APIs
-
performance and scalability matter
Industry reality:
Most organizations standardize on one framework, not all three.
Read More: Full-Stack Developer Career Path 2026
Career Level Expectations (Clear Differentiation)
Entry-Level Python Developer
-
understands core Python
-
can work with existing codebases
-
fixes bugs and implements small features
-
follows coding standards
Not expected:
-
system design decisions
-
architectural ownership
Mid-Level Python Developer
-
designs modules independently
-
writes APIs and database logic
-
understands performance implications
-
reviews code
Expected to:
-
solve non-trivial problems
-
contribute to system reliability
Senior / Lead Python Developer
-
owns technical decisions
-
designs system architecture
-
mentors other developers
-
balances scalability, performance, and maintainability
Focus shifts from coding volume to decision quality.
Professional Certifications: Practical Positioning
Certifications do not replace experience, but they can:
-
validate baseline knowledge
-
increase recruiter trust
-
improve visibility in early career stages
Relevant certification categories:
-
Python programming foundations
-
backend development with Python
-
API and web development
Certificates are most effective when paired with public projects or repositories.
Python Career Extensions After Entry-Level
Python enables multiple career expansions:
-
backend engineering
-
platform engineering
-
automation and DevOps tooling
-
data engineering
-
AI and machine learning pathways
Early specialization is not required. Strong fundamentals allow later transitions.
Salary Progression Overview
| Career Level | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Entry-Level | ₹4 – 8 LPA |
| Early Professional | ₹8 – 15 LPA |
| Mid-Level | ₹15 – 25 LPA |
| Senior / Lead | ₹25+ LPA |
| Global / Remote | $60k – $150k |
Salary growth correlates more with problem ownership and system knowledge than with number of tools learned.
How to Use This Roadmap Effectively
-
follow the learning order strictly
-
avoid parallel learning of unrelated topics
-
prioritize understanding over speed
-
build small, complete systems
-
evaluate progress by capability, not course completion
This roadmap is intended to be iterative, not linear.
Read More: Data Analyst Career Path 2026 – Skills, Roadmap & Courses
Affiliate Disclaimer: Some links in this post may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. These commissions help support the site — thank you for your support!




